As biometric authentication becomes integrated into our everyday lives, we want to look at which methods are most secure and which ones offer the highest level of practicality.
For most of us, biometric authentication is now a part of our daily lives, especially since smartphone manufacturers started to include biometric authentication as a security method for unlocking phones and apps. Each year, biometric authentication methods become more secure, whilst at the same time trying to make the experience for users a simple one.
Of course, biometric authentication goes well beyond smartphones. It is now widely used across a range of sectors as a way of managing access control, enabling services, catching criminals and keeping our borders secure.
In many cases, Biometrics have replaced the need to remember a password. However, we must consider how secure these new biometric technologies are and how we can ensure our biometric data is secure from identity theft and cyber criminals.
What are biometrics and what is biometric data used for?
Biometrics are a way to utilise a person’s physical characteristics to verify their identity and to answer a fundamental security question – are they who they say they are? Using biometric technology, a device’s security system can identify someone based on unique personal characteristics in a way that is extremely difficult if not impossible for hackers to replicate.
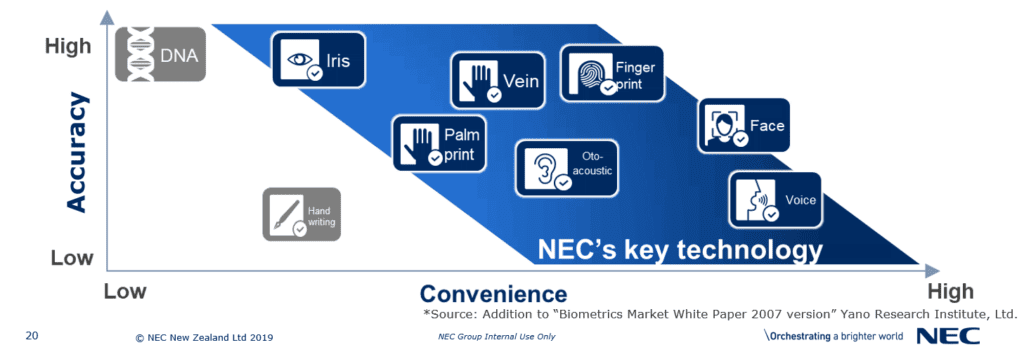
To be useful, biometric data must be unique, permanent and collectible. Once captured, the biometric is compared and matched in a database. Biometric security solutions include DNA, fingerprint, iris recognition, voice recognition, facial recognition and even behavioural characteristics like the way you type on a keyboard or user your computer mouse.
Beyond everyday functions like accessing your phone or apps, biometrics have many uses. For example, police can collect DNA and fingerprints at crime scenes or may use video security to analyse a suspect’s gait or voice.
In medicine, health exams may include retinal scans or genetic tests. Medical facilities are also using biometrics to authenticate individuals responsible for dispensing medicine and drugs to patients, helping to ensure only permitted personnel gain access to pharmaceuticals and to aid in ensuring that the correct doses are dispensed to the right patients.
Unlike other security measures such as passwords, keys and RFID badges, owners cannot lose biometric markers and they cannot be easily replicated or stolen by hackers. Whilst no security measure is completely safe from hackers, biometrics offer a layer of security within a network that is very difficult for hackers to exploit and one that is often convenient for the end user.
Types of Biometric Authentication
Let’s take the time to look more closely at the most common forms of biometric identification and look at some of the pros and cons of each method.
Facial Recognition
Fast, easy and convenient, facial recognition is a great option for consumers and many business users. Facial recognition is now included in the newest model smart phones as a security method for unlocking the device and it is widely used in places such as airports.
Facial recognition is a frictionless biometric that can be integrated into a multimodal approach utilising other biometrics or additional security tokens to provide even greater and faster authentication such as two factor authentication along with a password.
Pros
- Frictionless
- High speed
- Diverse applications
Cons
- Basic level facial recognition can lack accuracy
- Appropriate lighting and camera placement is important
Iris Recognition
Another contactless form of biometric authentication, iris recognition is starting to be included in smartphones, including the Samsung S8 and S8+ as a way of securely accessing the device.
Your iris is an extremely data-rich physical structure and contains a pattern that’s unique to each individual and virtually impossible to replicate. Additionally, because eyes are self-cleaning and image capture is performed without physical contact, readings are highly accurate and reliable.
Pros
- Contactless
- Flexible – works in light or dark conditions
- Separate eye recognition
- Fast and highly accurate
Cons
- Can cause issues for those who wear glasses
- Can have issues in direct sunlight depending on the scanner position
- May be difficult “from a distance” although this is improving
Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition is perhaps the most well-known and well-utilised of all biometric authentication methods. It has been around for the longest time on mainstream smartphones and is a great solution for many applications.
As well as practical applications such as smartphone security, fingerprint recognition technology has long been used by international airports for border protection and law enforcement agencies for public safety, capturing millions of fingerprints every day.
Fingerprint scanning on phones has become more sophisticated over time and the newest smartphones are now using Ultrasonic Fingerprint ID instead of traditional capacitive fingerprint sensors. Ultrasonic fingerprint ID offers a much greater degree of security and cuts down on the potential for 3D replicas.
Pros
- Highly accurate
- Integration with third party peripherals
- Fast database searching
- Mobile applications for use in the field by public safety officers
Cons
- Requires physical contact and therefore can’t be used “at a distance”
- Not practical in situations where people wear gloves
NEC and biometric security
At NEC, we place a strong focus on developing the most secure technology when it comes to biometric authentication. Across the biometric authentication methods discussed above, NEC ranks number one globally for both speed and accuracy for all three technologies and their applications.
Biometric technology is subject to rigorous independent testing by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and NEC consistently rank number one for our facial recognition, iris recognition and fingerprint recognition technologies.
Our R&D team works tirelessly to develop new ways to apply the technology and we regularly collaborate with our customers in order to generate new and innovative ideas. Our R&D team then fine tune the technology to help our customers achieve their business objectives.
You can read more about all of our biometric solutions here.
