Blockchain is causing a paradigm shift in the way individuals, businesses and governments conduct transactions.
Enabling transactions with security and trust, blockchain has the potential to trigger widespread digital transformation and create a far more digitally integrated global economy than what we have today.
While this technology presents significant opportunities for disruptive innovation across various industries, it’s still at a nascent stage.
With the technology rapidly evolving and its definition shifting, most people have inadequate and inaccurate knowledge of what blockchain really is.
In fact, there’s little consensus, let alone standardisation, even within the technical community.
Phase 1 in the evolution of blockchain: Public Ledger
Blockchain was developed in 2008 as the accounting method for Bitcoin.
The inventor of this game-changing technology is anonymous, going by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
Whether this is the name of a person, or a group of people is yet unknown.
Gradually, this technology was adopted to verify and keep track of different digital currency transactions without any central recordkeeping.
In its first phase, blockchain was a digitised and decentralised public ledger of transactions.
Here’s how it works:
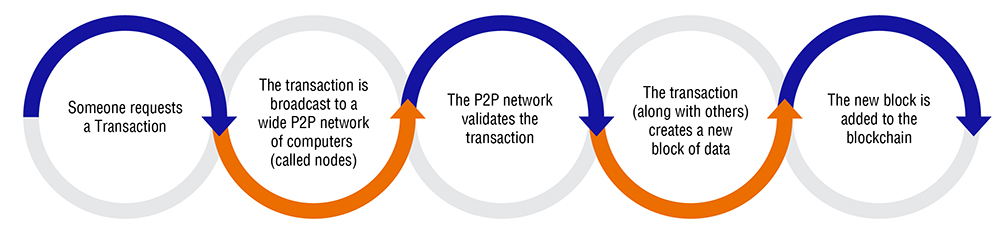
The main elements of public blockchain
The main elements of this revolutionary technology are:
- A shared database of transactions
- Decentralised (no central location where the database is stored)
- The storage and transmission of data takes place in coded form
- Relying on peer-to-peer networks
- Creates an indelible record of transactions
Despite the many advantages, this first phase of blockchain has certain drawbacks that limit its adoption by businesses.
- Not every business wants a public ledger. Blockchain being used for bitcoin transfers is not private; and leaks considerable information about its users.
- Recent news has shown the limits of decentralisation with just a few entities controlling mining and software development.
- Contrary to popular belief, this version of blockchain isn’t an immutable ledger. Several ledger changes have been made, the most notable being done by Ethereum following an attack by a hacker in June 2016.
- Blockchain being used for crypto transfers is independent of governance and regulations.
- Several attacks have been mounted on it and its security guarantees are still not fully understood.
- It’s based on proof-of-work, resulting in energy wastage and scalability limitations.
Phase 2 in the evolution of blockchain: Enterprise Use
Before long, it was recognised that blockchain can be used to create records of virtually anything of value.
Blockchain evolved for use by enterprises, which sought the many advantages this technology offered compared to traditional system architectures.
Types of enterprise blockchain
As described below, there are two kinds of enterprise blockchain.
- Private: Managed by a single company, where participants are internal users.
- Collaborative: Managed by two or more trusted organisations, based on consensus by a number of participants from each organisation.
In both these forms, blockchain comprises digital ledger entries that are distributed within a predefined infrastructure.
The distribution results in additional nodes (or layers) that provide consensus on each of the transactions.
Benefits of enterprise blockchain
The main benefit driving the increasing adoption of enterprise blockchain is that it is distributed.
It doesn’t rely on any central location where the database is stored.
This means:
- The records are easily verifiable
- The records are completely transparent
- There’s no centralised version that a hacker can attack and corrupt
- There’s no single point of failure
Another benefit of enterprise blockchain stems from the fact that it is based on consensus.
This ensures that:
- Any tampering is immediately identified
- Transactions once recorded cannot be altered
Other benefits of enterprise blockchain are:
- Facilitates collaboration and tracking of any and all kinds of transactions
- High security, using digital signatures and secure consensus technologies
- Removes the need for middlemen
- Eliminates the need to reconcile ledgers being maintained by different entities
- Cost advantages, due to elimination of middlemen and cost of validating transactions
The concept of smart contracts
The decentralised ledger can be used for smart contracts, which are essentially self-executing contracts.
These smart contracts can be used to exchange anything of value without the need for a middleman.
Here’s how it works:
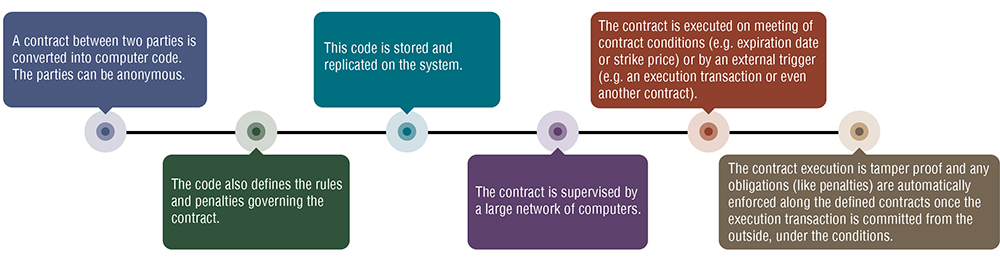
Leveraging enterprise blockchain
Blockchain makes transactions more secure and transparent.
The legacy banking and financial services industries are already facing the risk of serious disruption.
However, blockchain can be adopted by any industry that needs at least one of the following:
- A backend database
- A mechanism to exchange value
- Validation of contracts
- Maintaining online identities
The areas spearheading blockchain innovations are:
- Managing digital identities: Like birth certificates, marriage certificates, passports, social security numbers
- Property ownership: A recordkeeper of titles with time stamp that cannot be changed
- Healthcare: Access to different aspects of medical records to different entities
- Intellectual Property: Protection from piracy and IP infringement
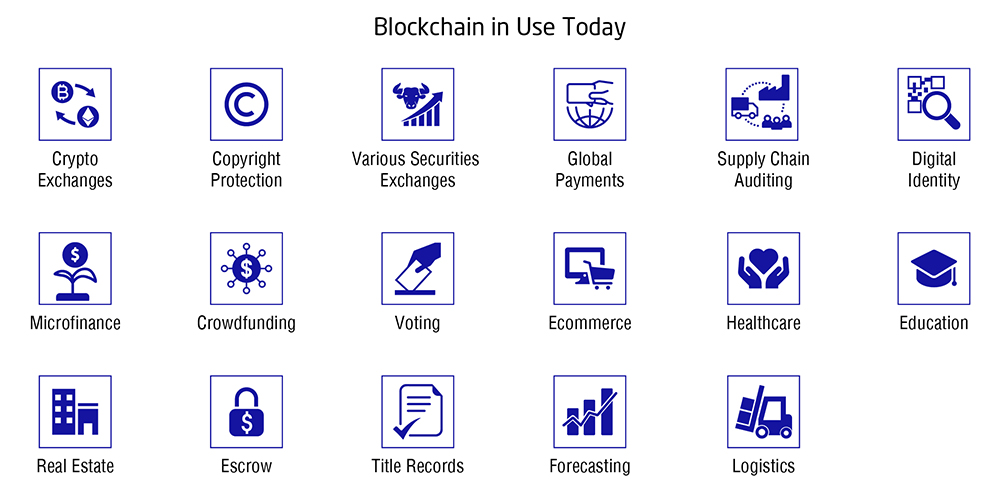
Blockchain in use today
Related Articles
You can find out more about NEC and blockchain technology on the global NEC site:
Blockchain for Digital Identity
This article was originally published on the NEC global website.
